The mechanism of deriving a new class from an old one is called inheritance. The old class is referred to as the base class and the new one is called the derived class or subclass. Inheritance is a mechanism of reusing and extending existing classes without modifying them, thus producing hierarchical relationships between them. C++ supports the following inheritance.
(a).Single Inheritance
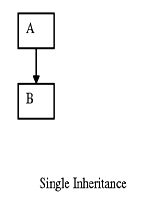
A derived class with only one base class is called single inheritance.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass {
int i;
public:
void setInt(int n);
int getInt();
};
class DerivedClass : public BaseClass {
int j;
public:
void setJ(int n);
int mul();
};
void BaseClass::setInt(int n)
{
i = n;
}
int BaseClass::getInt()
{
return i;
}
void DerivedClass::setJ(int n)
{
j = n;
}
int DerivedClass::mul()
{
return j * getInt();
}
int main()
{
DerivedClass ob;
ob.setInt(10); // load i in BaseClass
ob.setJ(4); // load j in DerivedClass
cout << ob.mul(); // displays 40
return 0;
}
(b) Multiple Inheritance
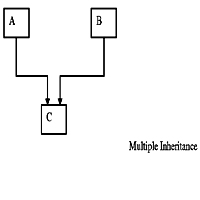
A derived class with several base classes is called multiple inheritance.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cpolygon
{
protected :
int width, height;
public:
void input_values(int one, int two)
{
width=one;
height=two;
}
};
class Cprint
{
public:
void printing (int output);
};
void Cprint :: printing (int output)
{
cout<<output<<endl;
}
class Crectangle: public Cpolygon, public Cprint
{
public:
int area ()
{
return (width * height);
}
};
class Ctriangle: public Cpolygon, public Cprint
{
public:
int area()
{
return (width * height / 2);
}
};
int main ()
{
Crectangle rectangle;
Ctriangle triangle;
triangle.input_values(2,2);
rectangle.input_values(2,2);
rectangle.printing(rectangle.area());
triangle.printing(rectangle.area());
return 0;
}
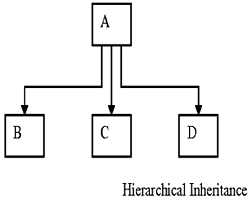
(c) Hierarchical Inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class student
{
protected:
int roll_no;
public:
void get_no(int a)
{
roll_no=a;
}
void put_no(void)
{
cout << “Roll No:”<<roll_no<<”\n”;
}
};
class test : public student
{
protected:
float part1,part2;
public:
void get_marks(float x,float y)
{
part1=x; part2=y;
}
void put_marks(void)
{
cout << “Marks obtained:” << “\n”
<< “Part1= “ <<part1<<”\n”
<<”Part2= “<<part2<<”\n”;
}
};
class sports : public student
{
protected:
float score;
public:
void get_score(float s)
{
score=s;
}
void put_score(void)
{
cout << “Sports wt:” <<score<<”\n\n”;
}
};
int main()
{
sports stud;
stud.get_no(1223);
stud.get_score(6.0);
stud. display();
return 0;
}
one class may be inherited by more than one class. This process is known as hierarchical inheritance.
(d) Multilevel Inheritance
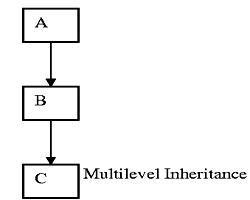
The mechanism of deriving a class from another derived class is known as multilevel inheritance.
********* IMPLEMENTATION OF MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE *********/
#include< iostream.h>
#include< conio.h>
class student // Base Class
{
protected:
int rollno;
char *name;
public:
void getdata (int b,char *n)
{
rollno = b;
name = n;
}
void putdata(void)
{
cout< < " The Name Of Student \t: "< < name< < endl;
cout< < " The Roll No. Is \t: "< < rollno< < endl;
}
};
class test:public student // Derieved Class 1
{
protected:
float m1,m2;
public:
void gettest(float b,float c)
{
m1 = b;
m2 = c;
}
void puttest(void)
{
cout< < " Marks In CP Is \t: "< < m1< < endl;
cout< < " Marks In Drawing Is \t: "< < m2< < endl;
}
};
class result:public test // Derieved Class 2
{
protected:
float total;
public:
void displayresult(void)
{
total = m1 + m2;
putdata();
puttest();
cout< < " Total Of The Two \t: "< < total< < endl;
}
};
void main()
{
clrscr();
int x;
float y,z;
char n[20];
cout< < "Enter Your Name:";
cin>>n;
cout< < "Enter The Roll Number:";
cin>>x;
result r1;
r1.getdata(x,n);
cout< < "ENTER COMPUTER PROGRAMMING MARKS:";
cin>>y;
cout< < "ENTER DRAWING MARKS:";
cin>>z;
r1.gettest(y,z);
cout< < endl< < endl< < "************ RESULT **************"< < endl;
r1.displayresult();
cout< < "**********************************"< < endl;
getch();
}
(e) Hybrid Inheritance
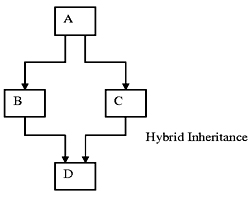
******** IMPLEMENTATION OF HYBRID INHERITANCE ********/
#include< iostream.h>
#include< conio.h>
class student
{
private :
int rn;
char na[20];
public:
void getdata()
{
cout< < "Enter Name And Roll No : ";
cin>>na>>rn;
}
void putdata()
{
cout< < endl< < na< < "\t"< < rn< < "\t";
}
};
class test : public student
{
protected:
float m1,m2;
public:
void gettest()
{
cout< < endl< < "Enter your marks In CP 1 And Cp 2 :";
cin>>m1>>m2;
}
void puttest()
{
cout< < m1< < "\t"< < m2< < "\t";
}
};
class sports
{
protected:
float score;
public:
void getscore()
{
cout< < endl< < "Enter your score :";
cin>>score;
}
void putscore()
{
cout< < score< < "\t";
}
};
class results : public test , public sports
{
private :
float total;
public :
void putresult()
{
total = m1+m2+score;
cout< < total;
}
};
void main()
{
results s[5];
clrscr();
for(int i=0;i< 5;i++)
{
s[i].getdata();
s[i].gettest();
s[i].getscore();
}
cout< < "______________________________________________"< < endl;
cout< < endl< < "Name\tRollno\tCP 1\tCP 2\tScore\tTotal"< < endl;
cout< < "----------------------------------------------"< < endl;
for(i=0;i< 5;i++)
{
s[i].putdata();
s[i].puttest();
s[i].putscore();
s[i].putresult();
}
cout< < endl< < "----------------------------------------------";
getch();
}