Runtime errors occur at the time the program executes and can't be corrected. A programmer can, however, take preventive measures while coding the program, to handle runtime errors with the help of the try, catch, and finally keywords.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace exception
{
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int x = 0;
int intTemp = 0;
try
{
intTemp = 100 / x;
Console.WriteLine("Not executed line");
Console.ReadLine();
}
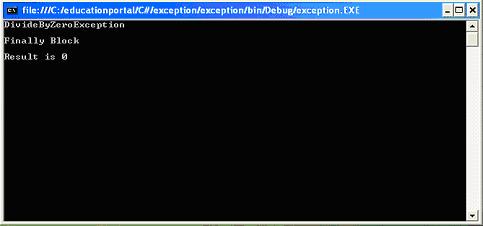
catch (DivideByZeroException de)
{
Console.WriteLine("DivideByZeroException");
Console.ReadLine();
}
catch (Exception ee)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception");
Console.ReadLine();
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("Finally Block");
Console.ReadLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("Result is {0}", intTemp);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
|


